Difference between revisions of "OpenInnovation"
(→Outside-In-Process) |
(→Inside-Out-Process) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=== Inside-Out-Process === | === Inside-Out-Process === | ||
| + | The Inside-Out-Process means the externalization of internal knowledge. It is used by companies to generate license fees for any patent or innovation. This kind of process | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Der Inside-Out-Prozess ist die Externalisierung von internem Wissen. Unternehmen nutzen diesen Prozess zum Beispiel, um Lizenzgebühren für Patente bzw. Innovationen einzunehmen, die sie nicht für die operative Geschäftstätigkeit nutzen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Der Inside-Out Prozess verdeutlicht, dass der Ort, an dem Wissen bzw. die Innovation entsteht, nicht mit dem Ort übereinstimmen muss, an dem die Innovation genutzt und in neue Produkte umgesetzt wird. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is also a possible combination of these two processes, which is called the '''Coupled-Process'''. | ||
== Application Areas == | == Application Areas == | ||
Revision as of 16:18, 3 December 2014
The term Open Innovation is based on the principle of Crowdsourcing. Thereby the process of innovation within organisations is open and the knowledge and skills of the crowd are used to optimize the innovation potential. The open-innovation-concept describes the functional use of the in- and out-going knowledge to improve innovation.
Contents
Motivation
In the running process of globalization grows the pressure on developers. The increasing opening of the procedure in competitions to everyone enables a growing number of solutions for products. Furthermore the life time cycle of innovation shortens more and more, so it becomes necessary that the wishes and the knowledge of the users become part of the developing process. The goal of Open Innovation should be to produce specific, target-oriented and useful products for the user.
Processes
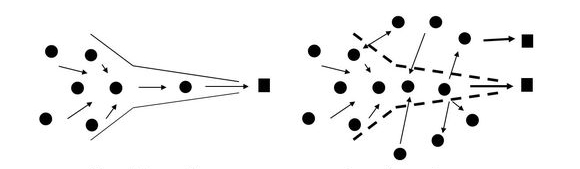
Closed innovation ...
- Closed Innovation -> Open Innovation (Quelle: BME - Innovationspotential von Lieferanten nutzen)
Outside-In-Process
The Ouside-In-Process describes the integegration of external knowledge to an innovation-process. With that instrument, the risk of a flopping innovation and the coherent economical dangers shall be minimized. This kind of process makes clear, that the place where Know-How is created must not be the same like where innovations are generated.
Inside-Out-Process
The Inside-Out-Process means the externalization of internal knowledge. It is used by companies to generate license fees for any patent or innovation. This kind of process
Der Inside-Out-Prozess ist die Externalisierung von internem Wissen. Unternehmen nutzen diesen Prozess zum Beispiel, um Lizenzgebühren für Patente bzw. Innovationen einzunehmen, die sie nicht für die operative Geschäftstätigkeit nutzen.
Der Inside-Out Prozess verdeutlicht, dass der Ort, an dem Wissen bzw. die Innovation entsteht, nicht mit dem Ort übereinstimmen muss, an dem die Innovation genutzt und in neue Produkte umgesetzt wird.
There is also a possible combination of these two processes, which is called the Coupled-Process.
Application Areas
Nowadays this type of innovation process is practiced in many areas of social and creative actions. Companies in design- and technical branches and even many polticians use the great knowledge of the crowd and involve the people in the innovation process.
Design
Politics
Technology
Literature
- Tayfun Belgin (Hrsg.): Christine und Irene Hohenbüchler – ... ansehen als ..., ... regarding as ... König u. a., Köln u. a. 2007, ISBN 978-3-9502333-0-8.
- Dorothee Messmer, Markus Landert (Hrsg.): Wilde Gärten. Christine und Irene Hohenbüchler. Niggli, Sulgen u. a. 2004, ISBN 3-7212-0523-5.
References
- (enter the word "references /" in two < >and this register will be created automatically, if you always used "ref" in two < > for your quotes and references in your paragraphs. If you still don't know how to use references, take a look at the backend.)