Difference between revisions of "Disputes in Crowdfunding"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The following article deals with disputes in | + | The following article deals with disputes in crowdfunding. |
| − | It covers several topics - who are the people and services involved, which are the possible disputes, what kind of legal background there is (which "Terms and Conditions" the [[platform]]s enforce). All the disputes are also further explained through examples of existing cases. | + | It covers several topics - who are the people and services involved, which are the possible disputes, what kind of legal background there is (which "Terms and Conditions" the [[Plattformen|platform]]s enforce). All the disputes are also further explained through examples of existing cases. |
| − | Up until 2014 there have been relatively few disputes in | + | Up until 2014 there have been relatively few disputes in crowdfunding, as that is a rather new thing. There are even less cases which went to court, because the risks of a lawsuit are too large and people are not prepared to lose their money over it. However, anyone who wishes to participate in online crowdfunding, should be aware of these possible risks, the disputes and frauds they might encounter. |
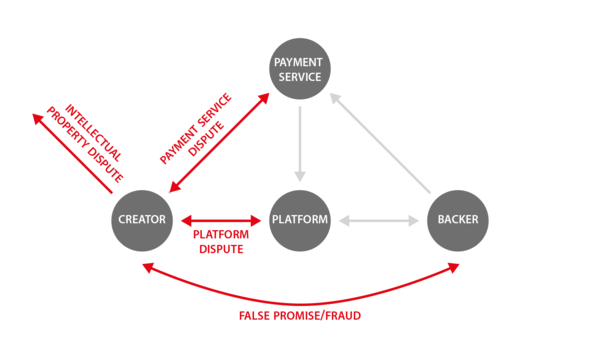
| − | There are four major groups of disputes - intellectual property disputes, false promises and frauds, [[platform]] disputes and payment service disputes. | + | There are four major groups of disputes - intellectual property disputes, false promises and frauds, [[Plattformen|platform]] disputes and payment service disputes. |
For those, who would like to read further and learn more than this article offers, there are some links to the websites where more detailed information can be found. | For those, who would like to read further and learn more than this article offers, there are some links to the websites where more detailed information can be found. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Involved Parties=== | ===Involved Parties=== | ||
| − | There are four different parties, which take part in all operating | + | There are four different parties, which take part in all operating crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s. From now on they will be referred to as creators, backers, [[Plattformen|platform]]s and the payment service. |
[[File:schema_disputes.png|center|600px]] | [[File:schema_disputes.png|center|600px]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Creators launch the campaign for a particular project with the objective of raising funds for the development of the suggested project. They can also be referred to as launchers, project owners, campaign owners, campaign launchers, project creators, uploaders etc. | Creators launch the campaign for a particular project with the objective of raising funds for the development of the suggested project. They can also be referred to as launchers, project owners, campaign owners, campaign launchers, project creators, uploaders etc. | ||
| − | Creators can be in one way or another involved in all of our suggested disputes - intellectual property disputes (presentation disputes, idea thefts, identity thefts, reselling scams), frauds (false promises to backers, launching non-existing projects), [[platform]] disputes ([[platform]]s can cancel the project at any time without any explanation) and payment service disputes (in which case creators are not directly involved, but they are the ones who suffer the damages). | + | Creators can be in one way or another involved in all of our suggested disputes - intellectual property disputes (presentation disputes, idea thefts, identity thefts, reselling scams), frauds (false promises to backers, launching non-existing projects), [[Plattformen|platform]] disputes ([[Plattformen|platform]]s can cancel the project at any time without any explanation) and payment service disputes (in which case creators are not directly involved, but they are the ones who suffer the damages). |
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
====Platforms==== | ====Platforms==== | ||
| − | [[Platform]]s are | + | [[Plattformen|Platform]]s are crowdfunding websites, which act as mediators between creators and backers. Creators upload their campaigns on [[Plattformen|platform]]s, where they can be seen by backers, who then decide if they would like to fund it. [[Plattformen|Platform]]s reserve rights to change or cancel the uploaded projects if they see fit and are protected by "Terms and Conditions", to which users must agree if they want to use the [[Plattformen|platform]]. Crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s usually take a certain percentage of the raised money (they collect for example 5% of the raised money, but most of them only do that if a project ends successfully). |
| − | The most popular | + | The most popular crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s currently are Kickstarter, Indiegogo, GoGetFunding, RocketHub, Crowdfunder, Crowdrise, Somolend, AngelList, Invested.in, Quircky etc. |
| − | [[Platform]]s distance themselves from any intellectual property disputes or possible frauds. They are, however, the main problem when it comes to - as we call it - [[platform]] disputes, as they reserve the right to change or cancel any project at any time for any reason, without having the obligation to explain why. In certain cases such actions led to the court, but due to the clearly stated Terms and Conditions, [[platform]]s are normally found not guilty of misconduct. | + | [[Plattformen|Platform]]s distance themselves from any intellectual property disputes or possible frauds. They are, however, the main problem when it comes to - as we call it - [[Plattformen|platform]] disputes, as they reserve the right to change or cancel any project at any time for any reason, without having the obligation to explain why. In certain cases such actions led to the court, but due to the clearly stated Terms and Conditions, [[Plattformen|platform]]s are normally found not guilty of misconduct. |
====Payment Service==== | ====Payment Service==== | ||
| − | Payment service is the intermediary, through which the donated funds are transferred from backers to creators. It is one of the online payment systems, for example PayPal or WePay, which facilitate the transfer of money between backers and creators, and they also take a cut for both the | + | Payment service is the intermediary, through which the donated funds are transferred from backers to creators. It is one of the online payment systems, for example PayPal or WePay, which facilitate the transfer of money between backers and creators, and they also take a cut for both the crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s and themselves. |
| − | Payment services are rarely involved in disputes, usually when their Terms and Conditions are not in accordance to those of the | + | Payment services are rarely involved in disputes, usually when their Terms and Conditions are not in accordance to those of the crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s. In those cases creators can successfully carry through their campaigns, but at the end they cannot receive the donated money because of the controversial content of the projects. |
===Platform "Terms and Conditions"=== | ===Platform "Terms and Conditions"=== | ||
| − | All | + | All crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s are protected by "Terms of use", which users have to accept if they wish to participate on the website. Although these Terms of use may vary from one [[Plattformen|platform]] to another, they all have a few main things in common. |
| − | All [[platform]]s clearly state, that by using their services you are agreeing to the terms and conditions of the website, which are then further explained. Most [[platform]]s protect themselves from any intellectual property issues, they have rules about what can and cannot be uploaded, they urge the users to respect the Third Party's (collaborating websites') Terms and Conditions. Most [[platform]]s also reserve the right to cancel, edit, reject, interrupt, suspend any project at any time for any reason. They distance themselves from any disputes between the different groups of users. | + | All [[Plattformen|platform]]s clearly state, that by using their services you are agreeing to the terms and conditions of the website, which are then further explained. Most [[Plattformen|platform]]s protect themselves from any intellectual property issues, they have rules about what can and cannot be uploaded, they urge the users to respect the Third Party's (collaborating websites') Terms and Conditions. Most [[Plattformen|platform]]s also reserve the right to cancel, edit, reject, interrupt, suspend any project at any time for any reason. They distance themselves from any disputes between the different groups of users. |
| − | [[Relevant sections from "Terms and Conditions"]] of three different [[platform]]s ([https://www.kickstarter.com/help/copyright Kickstarter], [https://www.indiegogo.com/about/terms Indiego], [http://gogetfunding.com/page/term-and-conditions GoGetFunding]) show the common points of all | + | [[Relevant sections from "Terms and Conditions"]] of three different [[Plattformen|platform]]s ([https://www.kickstarter.com/help/copyright Kickstarter], [https://www.indiegogo.com/about/terms Indiego], [http://gogetfunding.com/page/term-and-conditions GoGetFunding]) show the common points of all crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s. |
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
Main article: [[Platform Disputes]] | Main article: [[Platform Disputes]] | ||
| − | Platform disputes occur when project creators feel they have been mistreated by | + | Platform disputes occur when project creators feel they have been mistreated by crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s. Their campaigns are either cancelled, suspended or pauzed by [[Plattformen|platform]]s, in some cases without an obvious reason and explanation. |
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
Main article: [[Payment Service Disputes]] | Main article: [[Payment Service Disputes]] | ||
| − | Disputes involving payment services occur because of their and | + | Disputes involving payment services occur because of their and crowdfunding [[Plattformen|platform]]s' contrasting policies. The ones at loss are usually project creators, who are unable to receive the collected funds. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 12 December 2014
The following article deals with disputes in crowdfunding. It covers several topics - who are the people and services involved, which are the possible disputes, what kind of legal background there is (which "Terms and Conditions" the platforms enforce). All the disputes are also further explained through examples of existing cases.
Up until 2014 there have been relatively few disputes in crowdfunding, as that is a rather new thing. There are even less cases which went to court, because the risks of a lawsuit are too large and people are not prepared to lose their money over it. However, anyone who wishes to participate in online crowdfunding, should be aware of these possible risks, the disputes and frauds they might encounter. There are four major groups of disputes - intellectual property disputes, false promises and frauds, platform disputes and payment service disputes. For those, who would like to read further and learn more than this article offers, there are some links to the websites where more detailed information can be found.
Contents
General Information
Involved Parties
There are four different parties, which take part in all operating crowdfunding platforms. From now on they will be referred to as creators, backers, platforms and the payment service.
Creators
Creators launch the campaign for a particular project with the objective of raising funds for the development of the suggested project. They can also be referred to as launchers, project owners, campaign owners, campaign launchers, project creators, uploaders etc.
Creators can be in one way or another involved in all of our suggested disputes - intellectual property disputes (presentation disputes, idea thefts, identity thefts, reselling scams), frauds (false promises to backers, launching non-existing projects), platform disputes (platforms can cancel the project at any time without any explanation) and payment service disputes (in which case creators are not directly involved, but they are the ones who suffer the damages).
Backers
Backers are members of the public who financially back the projects by contributing funds. Backers can also be referred to as contributors, investors, funders, supporters etc.
Backers can be involved mostly in disputes over frauds (fraud from the creator - where they support a deceitful project, fraud by backer - where they promise funds, which they do not provide, or false promises - where they are promised rewards, which they do not receive).
Platforms
Platforms are crowdfunding websites, which act as mediators between creators and backers. Creators upload their campaigns on platforms, where they can be seen by backers, who then decide if they would like to fund it. Platforms reserve rights to change or cancel the uploaded projects if they see fit and are protected by "Terms and Conditions", to which users must agree if they want to use the platform. Crowdfunding platforms usually take a certain percentage of the raised money (they collect for example 5% of the raised money, but most of them only do that if a project ends successfully). The most popular crowdfunding platforms currently are Kickstarter, Indiegogo, GoGetFunding, RocketHub, Crowdfunder, Crowdrise, Somolend, AngelList, Invested.in, Quircky etc.
Platforms distance themselves from any intellectual property disputes or possible frauds. They are, however, the main problem when it comes to - as we call it - platform disputes, as they reserve the right to change or cancel any project at any time for any reason, without having the obligation to explain why. In certain cases such actions led to the court, but due to the clearly stated Terms and Conditions, platforms are normally found not guilty of misconduct.
Payment Service
Payment service is the intermediary, through which the donated funds are transferred from backers to creators. It is one of the online payment systems, for example PayPal or WePay, which facilitate the transfer of money between backers and creators, and they also take a cut for both the crowdfunding platforms and themselves.
Payment services are rarely involved in disputes, usually when their Terms and Conditions are not in accordance to those of the crowdfunding platforms. In those cases creators can successfully carry through their campaigns, but at the end they cannot receive the donated money because of the controversial content of the projects.
Platform "Terms and Conditions"
All crowdfunding platforms are protected by "Terms of use", which users have to accept if they wish to participate on the website. Although these Terms of use may vary from one platform to another, they all have a few main things in common. All platforms clearly state, that by using their services you are agreeing to the terms and conditions of the website, which are then further explained. Most platforms protect themselves from any intellectual property issues, they have rules about what can and cannot be uploaded, they urge the users to respect the Third Party's (collaborating websites') Terms and Conditions. Most platforms also reserve the right to cancel, edit, reject, interrupt, suspend any project at any time for any reason. They distance themselves from any disputes between the different groups of users.
Relevant sections from "Terms and Conditions" of three different platforms (Kickstarter, Indiego, GoGetFunding) show the common points of all crowdfunding platforms.
Types of Disputes
Disputes and frauds that occur in crowdfunding can be categorized into four groups depending on the subject of the dispute. In each of them there can be different involved parties. Most disputes occur between individual creators and backers, and are discussed and solved amongst themselves. These individuals are the most vulnerable, since most platforms and payment services protect themselves by their Terms of use.
Intellectual Property Disputes
Main article: Intellectual Property Disputes
Disputes over intellectual property include misuse of presentational material, idea theft, identity theft and reselling of an existing product. Most disputes occur over projects, which violate the patent, copyright or trademark rights of others, and over projects, which have not been lawfully protected.
Fraud and False Promise
Main article: Fraud and False Promise
Frauds and false promise disputes occur between project creators and backers. One of the two parties either fails to fulfill their promise, or does intentionally not deliver the reward.
Platform Disputes
Main article: Platform Disputes
Platform disputes occur when project creators feel they have been mistreated by crowdfunding platforms. Their campaigns are either cancelled, suspended or pauzed by platforms, in some cases without an obvious reason and explanation.
Payment Service Disputes
Main article: Payment Service Disputes
Disputes involving payment services occur because of their and crowdfunding platforms' contrasting policies. The ones at loss are usually project creators, who are unable to receive the collected funds.